

Youll need to look it up in a structural book or google it for more complete info. Where D_i=D-2t the inner, hollow area diameter. The moment of inertia (second moment of area) of a circular hollow section, around any axis passing through its centroid, is given by the following expression: The total circumferences (inner and outer combined) is then found with the formula: Its circumferences, outer and inner, can be found from the respective circumferences of the outer and inner circles of the tubular section. Įxpressed in terms of diamters, the plastic modulus of the circular tube, is given by the formula: The last formula reveals that the plastic section modulus of the circular tube, is equivalent to the difference between the respective plastic moduli of two solid circles: the external one, with radius R and the internal one, with radius R_i. We can also say from above equation of polar moment of inertia that, Polar moment of inertia of an element will be basically the resultant of the product of. Radius of gyration R_g of a cross-section is given by the formula: Where, D, is the outer diameter and D_i, is the inner one, equal to: D_i=D-2t.
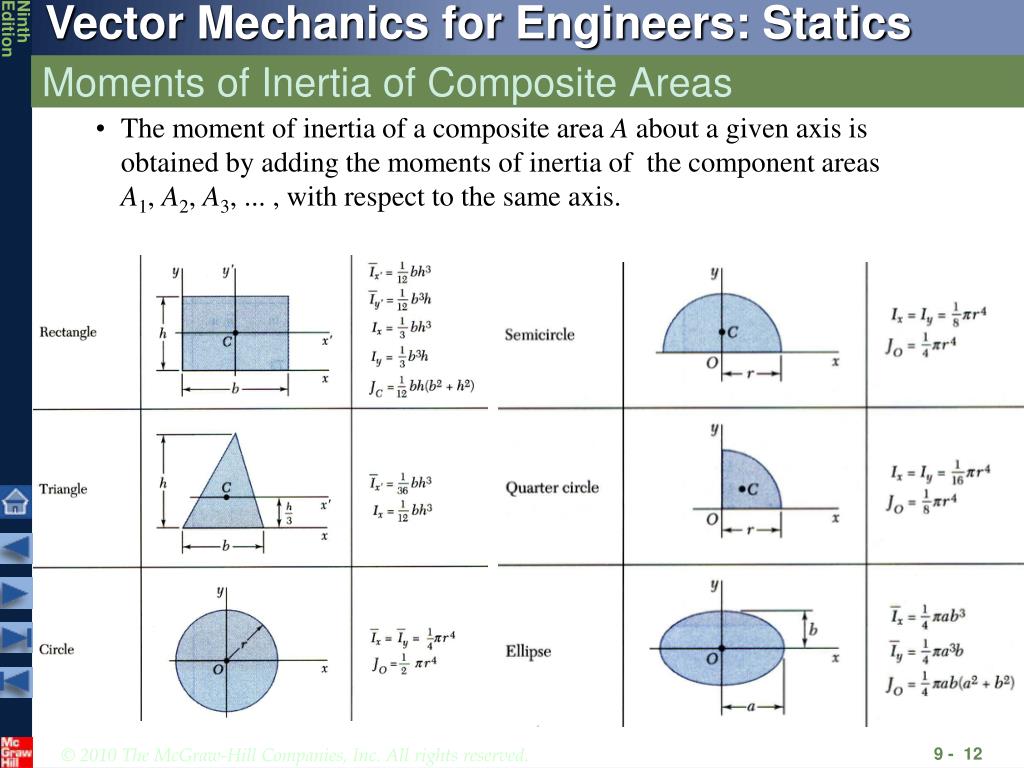
Where I the moment of inertia of the cross-section around a given axis and A its area. The dimensions of radius of gyration are.

It describes how far from centroid the area is distributed. Small radius indicates a more compact cross-section.Small radius indicates a more compact cross-section. Where I the moment of inertia of the cross-section about the same axis and A its area. Radius of gyration R g of a cross-section, relative to an axis, is given by the formula: Similarly, the plastic modulus of a rounded rectangle with respect to a centroidal axis y-y, perpendicular to its base, can be found, by alternating dimensions b and h, to the last formulas. \beginįor the above calculation, the cut-out corner area was considered as the difference of a square with side r and a quarter circle with the same radius.
The area A and the perimeter P of a rounded rectangle cross-section, having sides of length b, h and round corner radius r, are found with the next formulas:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
